Blackout in the Iberian penis on April 28, 2025: impact and analysis of the UPS market
Contesto: a blackout without precedents
On 28 April 2025, a blackout of historic proportions collapsed the Iberian peninsula, affecting Spain, Portugal, Andorra and some areas of southern France. The outage, which began at 12:33 a.m., left millions of people without power for about 23 hours, causing a devastating impact on critical infrastructure and daily life. Public transportation systems, such as trains and subways, have been affected; airports have suffered delays and cancellations; telecommunications networks have experienced widespread malfunctions, complicating communications and access to digital services.
The incident has highlighted the vulnerability of modern electricity grids, especially at a time when the transition to renewable energy sources and the increase in electricity demand require increasingly sophisticated management. Red Eléctrica de España (REE), the operator of the Spanish grid, has excluded the hypothesis of a computer attack, indicating as a probable cause an improbable loss of 15 gigawatts, equal to 60% of the current electricity production capacity. Such a disconnection could be due to a failure in the generation infrastructures, particularly in the solar energy sector, or to a grid instability caused by imbalances between demand and supply. The official investigations are still in progress to identify the cause and prevent future episodes.
Despite the chaos, some essential infrastructures continued to function thanks to emergency power supply systems, such as diesel generators and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). Hospitals have kept the outpatient and intensive care units operational; data centers have guaranteed the continuity of cloud services; the media have been able to transmit real-time updates; and airports have managed the flights in real time, even if chaotic ground traffic has complicated access to the facilities for the equipment. This event has underlined the crucial importance of UPS systems, and we are looking forward to analyzing the market for these technologies in 2024 to understand the investment trends and their strategic relevance.
Blackout impact and UPS performance
The blackout has had repercussions in many sectors, highlighting the dependence of modern societies on electricity. In Spain, the busiest cities, such as Madrid and Barcelona, have seen commercial activities paralyzed, with shops and restaurants forced to close or to operate with reduced capacity. Portogallo has reported similar problems, with Lisbona and Porto at presses with total blackouts that have interrupted public services. Even small realities, such as Andorra, have had significant problems, aggravated by their dependence on Spanish and French electricity grids.
UPS systems are essential to mitigate the effects of blackout. These devices, which provide temporary power in case of interruptions, have enabled critical infrastructures to maintain operational continuity. For example, data centers have prevented the loss of data and the interruption of cloud services, essential for companies and users in an increasingly digitalized world. In hospitals, UPS has ensured the operation of lifesaving machinery, while in air traffic control towers it has supported air traffic management, avoiding even more critical scenarios. However, the extended duration of the blackout has tested the capacity of many emergency systems, highlighting the need to invest in more robust and scalable solutions.
UPS market analysis in 2024
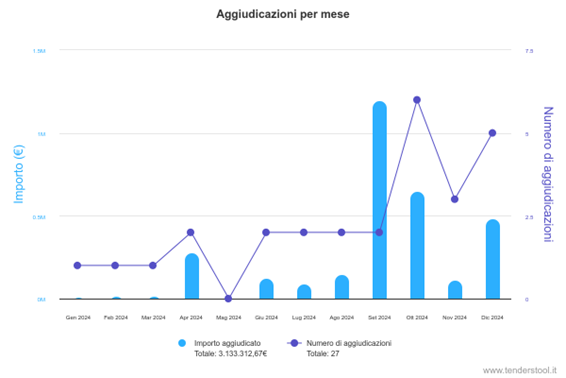
To understand the evolution of the UPS market and its strategic role, we have analyzed the data related to UPS technology applications in 2024, based on the monthly chronology of the acquisitions recorded on our platform. This analysis provides a snapshot of investment trends, sector priorities and regional dynamics.
Volume and time distribution of the appalti
In 2024, a total of 27 acquisitions were recorded for a total value of 3,133,312.67 euros. The subscription activity is concentrated in certain periods of the year, with two months that stand out in terms of volume and frequency:
- August 2024: The month with the highest amount recorded, exceeding 1.5 million euro. This small amount suggests an intense procurement activity, probably linked to large-scale infrastructure projects or to urgent needs for updating equipment.
- September 2024: The month with the highest number of contract awards (7 contracts), indicating a high dynamism in the closing of agreements, even with a lower amount compared to August.
Other months have shown a more contained activity, with periods of little or no allocation, suggesting a seasonal distribution of investments, probably influenced by balance cycles or project cycles.
Investment sectors and areas
The sectoral analysis shows a clear predominance of the DPC (Data Processing Center) infrastructure area, which accounts for most of the amounts allocated. This trend reflects the growing importance of data centers, which require advanced UPS systems to ensure operational continuity and protection against power interruptions. Other sectors, such as healthcare and transportation, account for a smaller but still significant share of investments.
Regional dynamics
Geographically, Italy shows an eterogeneous distribution of stocks:
- Emilia-Romagna: The region leads with a total amount of over 1.2 million euro, probably thanks to the presence of technology policies and critical infrastructures, such as data centers and university hospitals.
- Veneto: It is distinguished by the number of awards (7), indicating a higher frequency of contracts, even of lower amounts, compared to other regions.
Other regions, such as Lombardy and Campania, register significant activities but do not reach the levels of Emilia-Romagna and Veneto, suggesting a concentration of investments in areas with a strong technological or industrial vocation.
Main committents and contractors
The analysis of the stakeholders shows the role of public and academic entities in guiding investments in UPS technology:
- Università degli Studi di Salerno: With an amount of approximately 1.2 million euro, it is the main contractor, probably for projects related to research infrastructures or university data centers.
- Fondazione IRCCS Ca' Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico: Continues with about 0.8 million euro, reflecting the need for UPS systems to ensure the continuity of critical health services.
Three main actors emerge at the front end of the project:
- Zeta: Dominates with an amount of 709,684.47 euro, representing the most significant share of the total amount added.
- R1: Continues with 487,000.00 euro, occupying an important position but subordinate to Zeta.
- Siel: It contributes a lower amount, but remains among the main beneficiaries.
The distribution of the amounts is highly concentrated, with the first three bidders accounting for the largest share of the resources, while other operators account for progressively smaller shares.
Conclusions and future prospects
The blackout of 28 April 2025 in the Iberian peninsula has highlighted the criticality of electrical continuity systems in an increasingly interconnected and energy-dependent world. UPS systems have proved indispensable to limit damage, but the event has also revealed the need to invest in more resilient infrastructures and to plan more effective crisis management strategies.
The analysis of the UPS market in 2024 shows a growing settore, with concentrated investments in some areas and in strategic areas such as data centers. The Italian region, in particular Emilia-Romagna and Veneto, does confirm the policy of innovation, including the University of Salerno and large hospitals guided by the command of advanced technology. On the agricultural front, the predominance of some attori suggests a more competitive market with opportunities for new participants.
In order to deepen the data and trends, we invite you to consult our complete study, available on our website. At a time of growing energy challenges, investments in UPS systems are not only a necessity, but a strategic priority to ensure the resilience of infrastructure and the continuity of essential services.